GloNews10
The automobile industry in 2025 is undergoing a dramatic shift. Once hailed as the decade of electric vehicles (EVs), the dream of rapid EV adoption has slowed down in several major markets. This slowdown, often referred to as EV inertia, is caused by high vehicle costs, lack of charging infrastructure, and persistent range anxiety among consumers.
Instead of fully embracing EVs, many consumers are opting for hybrids and plug-in hybrid vehicles as a more practical solution. At the same time, autonomous vehicles are quietly gaining popularity—not necessarily as fully driverless cars, but through advanced driver-assist systems (ADAS) that make driving safer and more convenient.
This dual trend—EV inertia on one hand and autonomous vehicle enthusiasm on the other—is shaping the future of mobility across the globe.
EV inertia describes the slowdown in consumer enthusiasm for electric vehicles. While sales have grown over the past few years, the pace is not as strong as industry analysts once predicted. Several factors contribute to this trend:
Even with falling battery prices, EVs remain expensive compared to traditional vehicles and hybrids. For cost-sensitive markets, this is a major barrier.
A major obstacle is the lack of fast and reliable charging stations. In many regions, especially developing countries, EV owners cannot rely on consistent infrastructure.
Despite improvements in EV range, many consumers still fear running out of power on long trips. This psychological barrier continues to hurt adoption.
Potential buyers worry about long-term battery degradation and how it will affect resale prices. This uncertainty pushes many toward hybrids instead.
As EV inertia continues, hybrid and plug-in hybrid vehicles are becoming the go-to choice for millions of consumers. They offer a balance between efficiency and practicality.
Hybrids allow drivers to enjoy better fuel efficiency while eliminating range anxiety, making them the “bridge technology” of this decade.
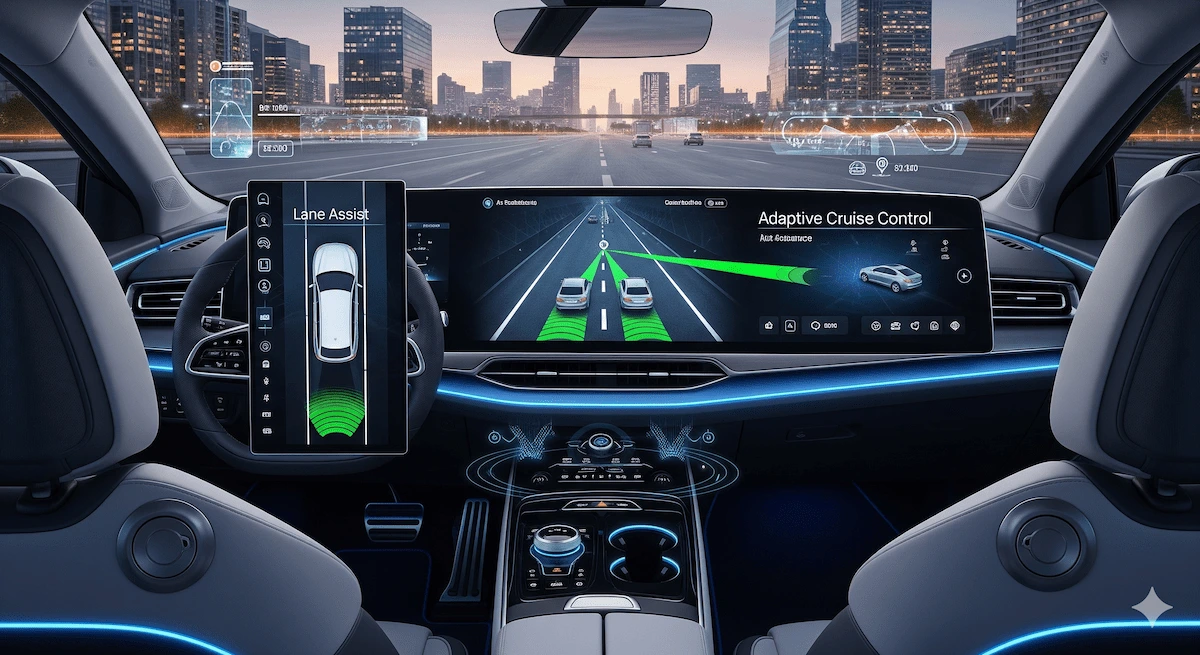

While EV adoption slows, autonomous vehicles are experiencing growing excitement. Instead of waiting for fully self-driving cars, consumers are embracing incremental autonomous features that improve safety and convenience.
These features are now common in mid-range and luxury cars, and they appeal to consumers who prioritize safety.
According to recent global consumer trends, the automobile industry will not be dominated by one single technology. Instead, it will be shaped by:
This indicates that consumers value practicality, safety, and affordability more than futuristic promises.
Automakers must recognize this consumer shift and adapt their strategies accordingly:
Companies that balance all three—EVs, hybrids, and autonomous technologies—will lead the global market.
Looking ahead, several scenarios are likely:
The global automobile industry in 2025 is marked by two powerful forces: EV inertia and the rise of autonomous vehicles. While the adoption of electric cars is slowing due to cost and infrastructure challenges, hybrids are stepping in to fill the gap. Meanwhile, autonomous vehicle features are winning consumer trust by making driving safer and easier.
For automakers, the message is clear: the future is hybrid, connected, and increasingly autonomous. Companies that adapt to these global consumer trends will define the next chapter of mobility.