GloNews10
The United States government is a complex machine, built upon a carefully balanced structure, yet its policies create immediate, global ripples. For any reader, investor, or global citizen, understanding US Federal Policy is no longer optional; it’s essential for anticipating market shifts and social changes.
As we dive into 2025, the landscape is dominated by critical legal battles surrounding Voter Suppression laws and the rapidly changing Election Policy Trends that determine who holds power.
We’ll break down the roles of the Executive, Legislative, and Judicial branches, analyze how laws are enforced via Federal Regulations, and examine the global impact of key debates, including highly charged Immigration Policy and the ongoing Redistricting Battle. This guide is your definitive resource to master the structures that shape the world’s most powerful political system.
The United States government is a complex machine, built upon a carefully balanced structure to ensure no single entity wields absolute power. For any global citizen or investor, understanding US Federal Policy is no longer optional; it’s essential for anticipating market shifts and social changes. As we look into 2025, the landscape is dominated by critical questions surrounding Voter Suppression laws, rapidly changing Election Policy Trends at the state level, and the ongoing debates over national Immigration Policy.
This guide is your definitive resource to break down the core structure of US governance, dissect how Federal Policy is created and enforced, and analyze the immediate impact of key laws and electoral battles on citizens and the world stage. By mastering these foundational concepts, you gain the ability to predict the political moves that shape the Global Economy and your own financial future.
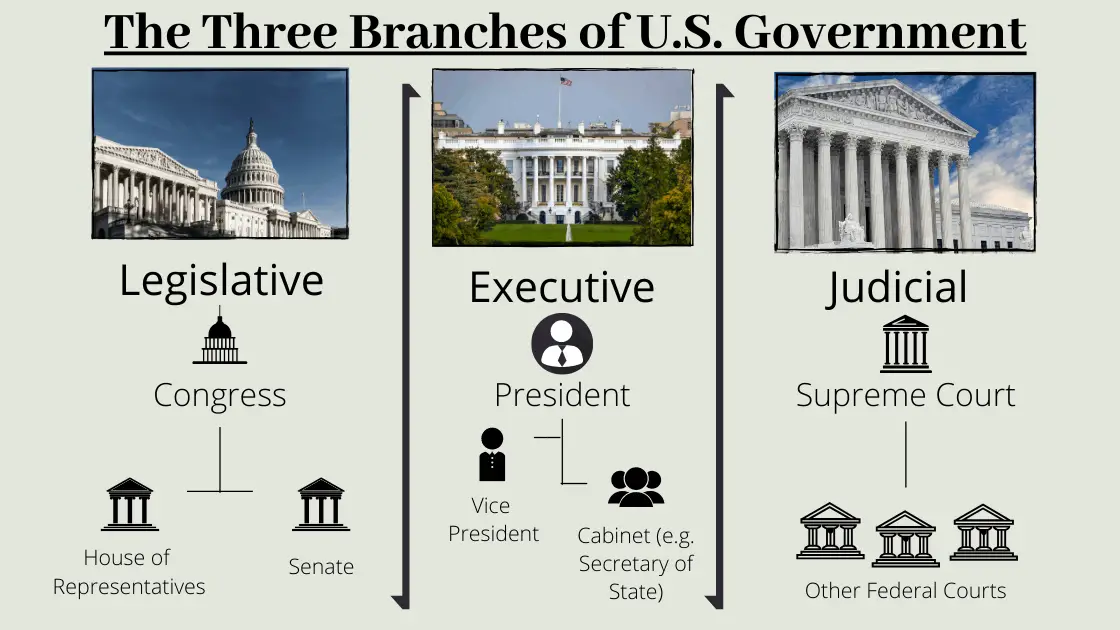
The US system operates on the principle of “separation of powers,” distributing authority among three branches to prevent tyranny and ensure checks and balances.
This branch, known as Congress, is the primary authority for creating laws and authorizing spending. It is composed of the Senate and the House of Representatives.
Role in Policy: Congress holds the “power of the purse,” meaning it authorizes all federal expenditures, from military spending to social programs. Every major Federal Policy must originate as a bill and be approved by both chambers.
Key Issues Driving Headlines in 2025:
Headed by the President, the Executive Branch is tasked with executing and enforcing the laws passed by Congress. This is where most federal employees work, administering government services.
Role in Policy: The President influences the direction of Federal Policy through Executive Orders and by appointing heads of federal agencies (such as the EPA or the Department of Health). These agencies then write the specific Federal Regulations that make the laws actionable.
Policy Focus Area: Immigration Policy: One of the most visible areas of executive influence is Immigration Policy. The administration can dramatically alter enforcement priorities, shift resources to the border, and change visa procedures (like the recent H-1B Visa Fee Hike) with immediate executive action.
This branch comprises the Supreme Court and lower federal courts. Its critical role is to interpret the Constitution and review the legality of laws and executive actions.
Key Issue: Election Policy and Law: In 2025, the courts are the central battleground for Election Policy Trends. Judicial decisions on voting laws, ballot access, and campaign finance define the rules of democracy itself.
Policy isn’t instantaneous. It follows a predictable, though often slow, cycle. Understanding this cycle is essential for investors and citizens who need to anticipate government moves.
This section details the formal journey of a law:
Once a law is passed, its actual effect is determined by the Federal Regulations written by agencies like the Department of Treasury or Department of Commerce.
Elections are the engine of change. The rules surrounding them are constantly under scrutiny, making them a primary focus of US Federal Law.
The 2020 election cycle intensified the debate over Voter Suppression. This is a major area of concern because it directly challenges the fundamental tenet of democracy: the right to vote.
The Redistricting Battle occurs every decade after the census. It determines which party holds power by drawing electoral maps.
The laws governing how political campaigns are funded are constantly in flux. The Supreme Court’s past decisions on campaign finance continue to shape the financial power of special interest groups and individual donors, linking wealth directly to policy influence.
The US is a global superpower, and its domestic policies rarely remain confined to its borders. This section emphasizes the “Glo” in Glonews10.
The Executive and Legislative branches in Washington do not legislate in a vacuum; their decisions are the primary drivers of global stability, international trade, and diplomacy.1 For any global investor or citizen, tracking the shifts in US Foreign Policy is essential, as these moves can open or close entire markets overnight.
The US maintains its global dominance largely through a network of treaties and alliances forged after World War II.
The global news cycle is often driven by the US response to international crises.
Federal Policy regarding international trade is a primary driver of global economic volatility.
US Federal Policy on Climate Change (like emissions standards or renewable energy incentives) creates ripples across international agreements and global corporate compliance standards. Similarly, US funding for global health initiatives (like those related to Diabetes or Vaccinations) shapes the worldwide response to health crises.
The “Definitive Guide to US Federal Policy, Elections, and Law” demonstrates that the US political system is a dynamic and high-stakes environment. From the micro-level of Voter Suppression laws to the macro-level of Federal Policy 2025, every decision affects the global political and financial landscape.
For the readers of Glonews10, the key is not just to consume the news, but to understand the underlying structures. By tracking the Election Policy Trends debated in the courts and the Immigration Policy enforced by the Executive, you can stay ahead of the curve.